In recent years, restrictions on single-use plastics have been tightening worldwide. In Europe, the Single-Use Plastics Directive (2019/904) came into effect in 2021, requiring member states to gradually phase out non-recyclable single-use plastic products, including plastic-lined beverage cups [EU, 2019/904]. In 2024, the U.S. FDA also revoked 35 food-contact authorizations related to PFAS, signaling the phase-out of plastic-coated paper cups and containers [FDA, 2024]. At the same time, countries like Canada and India have also introduced bans on single-use plastics, further accelerating the adoption of eco-friendly alternatives.

Against this backdrop, the food packaging industry is facing unprecedented transformation pressure. Brands, wholesalers, and suppliers are all looking for one critical answer: how to find a paper cup solution that is waterproof and grease-resistant while fully compliant with eco-regulations?
The Aqueous Cup—also known as the aqueous paper cup—has emerged as an innovative green alternative. It is now seen as the ideal replacement for traditional PE, PP, and PLA-lined cups. In this guide, GMZ’s cup manufacturing experts will walk you through: What is an aqueous cup? How does its barrier coating work? And what are its core features?
What is an Aqueous Cup?
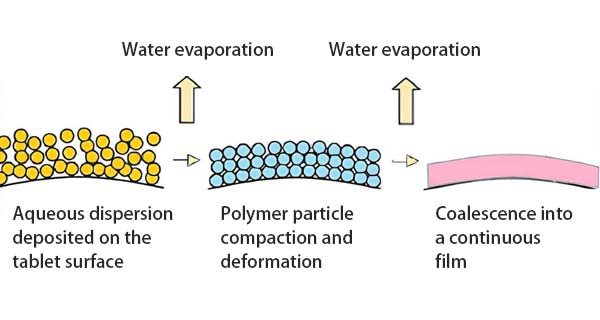
An Aqueous Cup is an eco-friendly paper cup that uses an aqueous coating on the inner wall of the paperboard as its barrier layer. Unlike traditional paper cups lined with PE (polyethylene) or PLA (polylactic acid), an aqueous cup applies a water-based dispersion coating. During production, water acts as the main dispersing medium, allowing the coating materials to evenly attach to the paper surface and form a dense protective film.
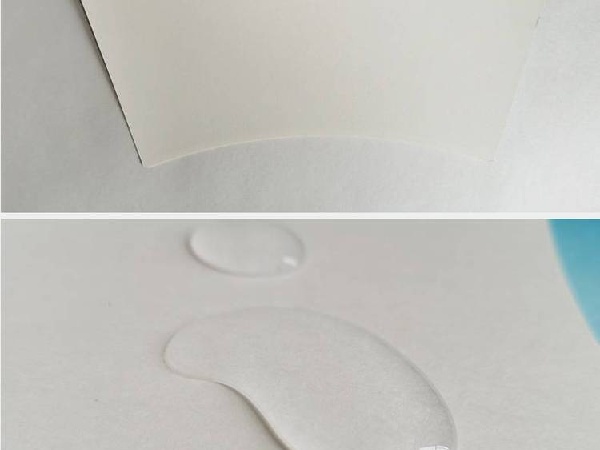

This coating works by creating a continuous polymer barrier layer over the paper fibers, preventing liquid penetration. It provides water-, oil-, and moisture-resistance while keeping the paperboard lightweight yet structurally strong. Unlike plastic linings, aqueous coatings are much easier to separate from paper fibers during recycling, making them more compatible with existing paper recovery systems.
Core Features of Aqueous Paper Cups
The core features of aqueous paper cups can be summarized in four key points:
- Waterproof and grease-resistant: Effectively prevents leakage from hot or cold drinks, soups, or oily foods.
- Recyclability: Can enter standard paper recycling streams without requiring complex processes.
- Food safety: Meets FDA and EU food-contact standards, free from PFAS and other harmful substances.
- Eco-friendly attributes: Reduces reliance on traditional plastics and minimizes composite paper-plastic waste, helping brands meet tightening global environmental regulations.

With stricter environmental rules and rising consumer awareness, aqueous cups are rapidly becoming the go-to solution for the disposable paper cup industry.
How Are Aqueous Cups Manufactured?
The production process of an aqueous cup is similar to that of a traditional paper cup, with one major difference: the coating stage. Using food-grade pulpboard as the base material, the paper is first cut and pretreated to ensure a clean, smooth surface. Then, through a water-based coating process, aqueous polymer dispersions are evenly applied to the inner wall of the board using techniques such as blade coating, roller coating, or rod coating.
Unlike PE extrusion lining, aqueous coatings use water as the dispersing medium. In hot-air or infrared drying systems, the water evaporates quickly, leaving behind a dense and continuous barrier layer.

Once the coating is cured, the paperboard moves to the forming stage, where it is rolled, pressed, and heat-sealed into the final cup shape. This process eliminates high-temperature plastic extrusion, cutting down on both energy consumption and plastic content. As a result, aqueous cups are much easier to separate from paper fibers during recycling, improving both pulp recovery rates and eco-value.
Why Are Aqueous Cups More Eco-friendly?
Compared to traditional PE-lined paper cups, aqueous cups offer clear advantages in terms of recycling. Because aqueous coatings contain little to no plastic, they separate from paper fibers more easily during pulping. Studies show that paper cups using water-based polyacrylate coatings perform exceptionally well in recycling, with fiber recovery efficiency far higher than that of PE or PLA-lined cups. In fact, the industry generally recognizes that aqueous cups can reach a pulp recovery rate of 80–90%.
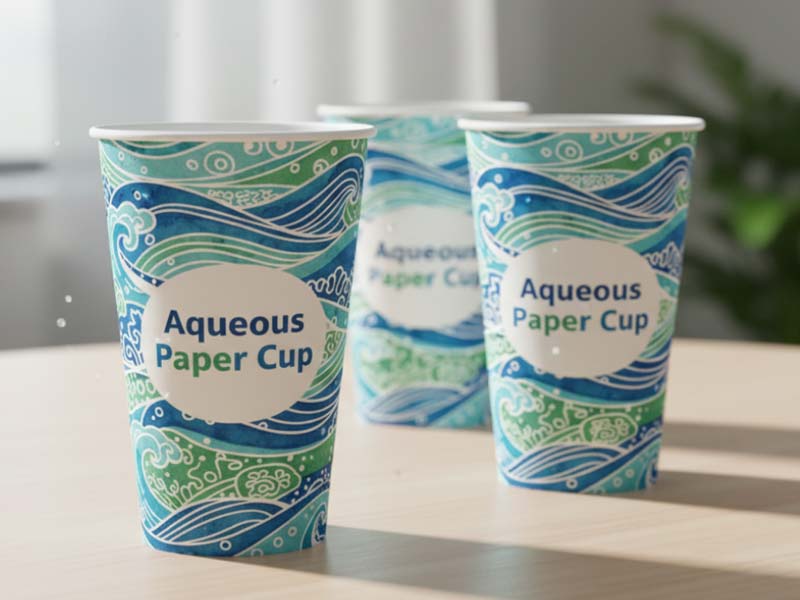

This means that in natural environments, the paperboard of an aqueous cup decomposes like ordinary paper, typically within weeks to months. The coating itself varies depending on the formulation, but overall, it breaks down much faster than PE linings and does not require specialized industrial composting. As a result, aqueous cups remain relatively eco-friendly even when waste sorting is insufficient or when discarded into nature.
Thanks to their recyclability and faster degradation, aqueous cups are widely seen as a breakthrough in the sustainable transition of disposable paper cups.
Aqueous Cup vs. PE/PP/PLA Lined Cups
To help you better understand the features of aqueous cups, let’s compare them with the more common PP, PE, and PLA cups. The following table highlights the key differences across seven aspects:
| Feature | Aqueous Cup | PP Cup | PE Lined Paper Cup | PLA Lined Paper Cup |
| Main Material | Food-grade pulpboard + aqueous coating | 100% polypropylene plastic | Food-grade pulpboard + PE lining | Food-grade pulpboard + PLA lining |
| Water/Oil Resistance | Excellent | Moderate (best for cold drinks) | Excellent | Excellent |
| Heat Resistance | Good (suitable for hot & cold drinks) | Poor (deforms with hot drinks) | Good (heat-friendly) | Moderate (some limits for hot drinks) |
| Eco Attributes | Recyclable; fits regular paper recovery streams | Partially recyclable, low recovery rate | Difficult to recycle, paper-plastic composite | Compostable, but only under industrial conditions |
| Cost Level | Slightly higher than PE, lower than PLA | Low | Low | High |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meets FDA/EU food safety standards; future-proof | Plastic use restricted | Facing strict bans (e.g., EU SUPD) | Meets some eco standards, but limited adoption |
| Typical Applications | Coffee, tea, fast food, takeout, ice cream cups | Milk tea, juice, smoothies | Coffee, tea, fast food cups | Eco events, some coffee shops |
1. PP Plastic Cup
Made entirely of polypropylene, PP cups are most common in transparent cold drink packaging such as milk tea, juices, or smoothies. They are lightweight, low-cost, and resistant to cold. However, from an environmental standpoint, they fall short—plastic recovery rates remain low, and most cups end up in landfills or incineration, leading to a much higher carbon footprint compared with paper cups.
2. PE Lined Paper Cup
These cups offer excellent leak-proofing and heat resistance. With mature production and low costs, they have long dominated the market. However, the tight bond between paper and plastic makes them nearly impossible to recycle in standard systems, leaving incineration or landfill as the primary disposal methods.
3. PLA Lined Paper Cup
PLA comes from renewable resources such as corn or sugarcane. It provides similar water and oil resistance to PE and is often promoted as an eco-friendly option. But there’s a catch: PLA requires industrial composting facilities to break down. Without them, it lingers much like conventional plastics. Its higher cost has also limited large-scale adoption.
4. Aqueous Cup
By contrast, aqueous cups meet both hot and cold drink needs while easily separating from paper fibers during recycling. They fit directly into existing paper recovery systems. Unlike PP with its “plastic burden,” PE with its “recycling challenge,” and PLA with its “high cost and composting limits,” aqueous cups strike a better balance—practical, eco-friendly, and aligned with future regulations.

FAQs About Aqueous Cup
1. Is aqueous coating food safe?
Yes. Aqueous coatings undergo strict food-contact safety testing and comply with both FDA and EU standards. They are free from PFAS and other harmful substances, making them safe for hot drinks like coffee or tea, as well as cold beverages and food packaging.
2. What is aqueous coating made of?
Aqueous coatings are typically formulated from water-based polymer emulsions such as modified acrylics and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA). Using water as the dispersion medium, they are applied to the paperboard surface to form a waterproof, grease-resistant protective layer—without relying on traditional plastics.
3. Does the coating process affect performance and cost?
Yes. The coating method (blade, roller, or rod coating), formulation, and drying process all directly influence leakage resistance. When applied evenly and cured properly, the coating provides excellent waterproofing and oil resistance.
However, if the layer is too thin or insufficiently dried, seepage may occur. Manufacturers may also adjust ratios of acrylics, PVA, or starch/cellulose derivatives. The more optimized and cured the formula, the better the heat resistance and barrier properties—though costs will rise accordingly.
4. How much do aqueous cups cost?
Aqueous cups are slightly more expensive than traditional PE-lined cups, but the gap is shrinking with scaling and better technology. Current prices typically fall between PE and PLA cups. For bulk orders, costs can be further reduced. For a detailed price comparison, you can contact GMZ for wholesale quotes and coating options.
5. Can aqueous cups replace traditional coffee cups?
Absolutely. With improved production techniques, aqueous hot cups can now reliably handle coffee, tea, and other hot drinks. Many coffee chains are already testing or adopting them to meet eco-regulations and strengthen brand image. Manufacturers like GMZ are partnering with coffee brands to deliver recyclable aqueous hot cup solutions.

6. Why have aqueous cups become more important in recent years?
Beyond stricter regulations and rising eco-consciousness, supply chains have matured, lowering costs. The coffee market also plays a decisive role. Reports show paper cups already account for over 60% of the disposable cup market, with hot beverages—especially coffee—dominating in many regions. This makes aqueous coffee cups a clear trend in the next wave of disposable cup solutions.

Conclusion
We hope this article has given you a clear and comprehensive understanding of the aqueous cup. With global environmental regulations becoming stricter and consumer awareness rising, choosing the right eco-friendly paper cup solution is no longer just a trend—it is the key for businesses to stand out in a competitive market. As a solution that combines both eco-performance and practicality, the aqueous cup is rapidly becoming the industry’s direction of choice.
If you still have questions, feel free to consult GMZ’s paper cup experts. Our team is ready to provide professional answers and technical support. And if you are looking for a reliable wholesale supplier of aqueous cups, GMZ can deliver certified, customizable products to help you quickly gain an edge and win customer trust in today’s eco-driven and competitive environment. Contact GMZ today!














